If you’ve been trying to find out how to stop your hair from falling out, you’re not alone. Male pattern baldness, scientifically known as androgenetic alopecia, is the most common cause of hair loss worldwide.
According to the U.S. National Library of Medicine, androgenetic alopecia is estimated to affect around 50 million American men, making it the most common type of baldness. Its causes are, in part genetic, distinguishing it from other forms of hair loss.
A study in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings reported that:
- Approximately 20 percent of men under 25 years old will notice the earliest signs of balding.
- By the age of 35, around 40 percent of men will experience some hair loss.
- Meanwhile, 50 percent of men will have significant hair loss by the time they reach 50 years of age.
Once you’ve sorted through the facts and separated them from the marketing fluff, you’ll be left with just a handful of clinically-proven and scientifically-sound options. One of the most popular options is finasteride.
What is finasteride?
Finasteride is an oral treatment for male pattern baldness. According to a study in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, it was medically approved in 1997 by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration after research demonstrated how it could help prevent hair loss in men. There is also ongoing research about finasteride being used to treat patterned hair loss in women. Finasteride works for many people, but can come with some significant and potentially permanent side effects.

Finasteride can come in different doses, shapes, and sizes
How does finasteride work?
You’ve probably heard of the male sex hormone, testosterone. Harvard Health Publishing says that this hormone is necessary for the changes boys experience during puberty, like a deepening voice or growing genitals and more body hair. It’s also vital for health in adult men, moderating bone density, muscle growth, and sex drive.
Male sex hormones increase the growth of body hair, but ironically, too much testosterone can cause hair loss on the scalp. This is hardly what you’d expect as a manly side-effect from this hormone.
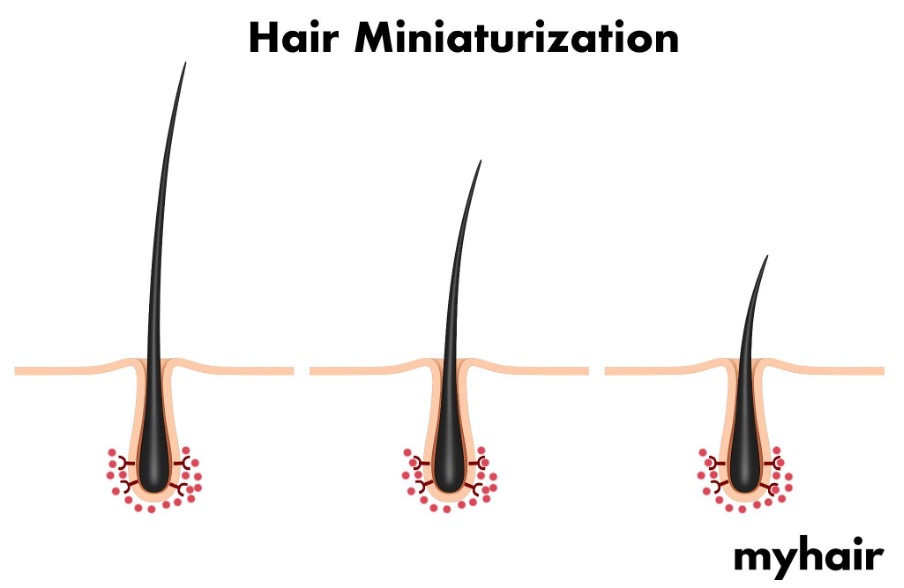
When testosterone comes into contact with an enzyme in the body called 5-alpha reductase (5-αR), it is catalyzed into another more potent male sex hormone called dihydrotestosterone (DHT). A study in the Plastic Reconstructive Surg Journal says that elevated levels of this hormone have been associated with male pattern hair loss. DHT attaches itself to receptors on the hair follicles in your scalp and affects hair growth.
Finasteride helps to lower DHT if your body is producing too much. It does this by interrupting the conversion of testosterone into DHT, specifically blocking the 5-αR enzyme responsible for the process. As a result, there is less DHT in the body to bind to receptors and affect hair growth.
Should I take finasteride?
Finasteride is available as a prescription medication. According to the U.S. National Library of Medicine, it comes in pill form and is usually taken once per day. It’s best to be consistent and patient, as you usually only see its benefits after a few months.
Finasteride also typically needs to be taken indefinitely. If you stop, your new hair growth will be stunted, and eventually, it will be reversed.
Finasteride side effects
Be aware of potential finasteride side effects before you choose to start using this product. Some side effects can be quite severe and might impact your lifestyle negatively. Certain side effects may even be permanent. These side effects can include sexual dysfunctions, like:
- Lower libido and lack of interest in sex
- Erectile dysfunction
- Abnormal ejaculations
- Testicular pain
- Decreased semen quality
Other side effects may also occur, including:
- Changes to breast tissue
- Nipple discharge
- Swelling around your lips or other parts of your face
- Itchy skin
- Skin rashes or hives
It’s always important to weigh the benefits of any medication against its side effects. Due to finasteride’s impact on their hormonal balance and sex life, many men have opted for other treatments that don’t have the same downsides.
If you’re considering using finasteride, it might also be useful to learn about a condition called post-finasteride syndrome. According to an article in the International Journal of Trichology and the Post-Finasteride Syndrome Foundation, the medical community has not yet accepted post-finasteride syndrome as a condition. However, recent research, including a report published in the Neurobiology of Stress, considers this to be an emerging problem that can cause serious side effects.
Accounts from finasteride users describe a persistent, sometimes permanent condition that causes physical, mental, and sexual symptoms even after stopping use. For more information, it’s best to consult your doctor and a dermatologist or trichologist.
Takeaway
Finasteride is an FDA-approved hair loss treatment that can help combat androgenic alopecia. However, due its wide range of side effects, it’s not for everyone.
If you’ve experienced finasteride side effects or are concerned about post-finasteride syndrome, there are a variety of other hair loss treatments you could try, including minoxidil, microneedling, or low-level laser therapy. There are even supplements, nutrients, and foods that can help support hair growth and prevent hair loss.