Do DHT blockers really work? In short – definitely! In fact, finasteride – one of the most popular hair loss treatments and the only oral, FDA-approved medication for androgenic alopecia – is actually a DHT blocker.
Androgenic alopecia has both genetic and hormonal components that cause balding. DHT, otherwise known as dihydrotestosterone, is the hormonal component that’s thought to be one of the main causes behind this condition. Blocking this hormone can stop androgenic alopecia’s progression and prompt hair regrowth.
What is DHT?
DHT (dihydrotestosterone) is a hormone and a sex steroid. As it’s full name implies, it’s related to the main male sex hormone, testosterone.
DHT is essentially created from testosterone through a conversion process. The conversion from testosterone to DHT is done by an enzyme family that’s known as 5-alpha reductase (5-αR).
According to a study in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology, DHT is essential for normal male development. However, in large quantities, DHT can also cause a variety of health problems. Excess amounts of this hormone have been associated with:
- Acne
- Androgenic alopecia (male pattern baldness)
- Enlarged prostate
- Excessive body hair growth
DHT and hair loss
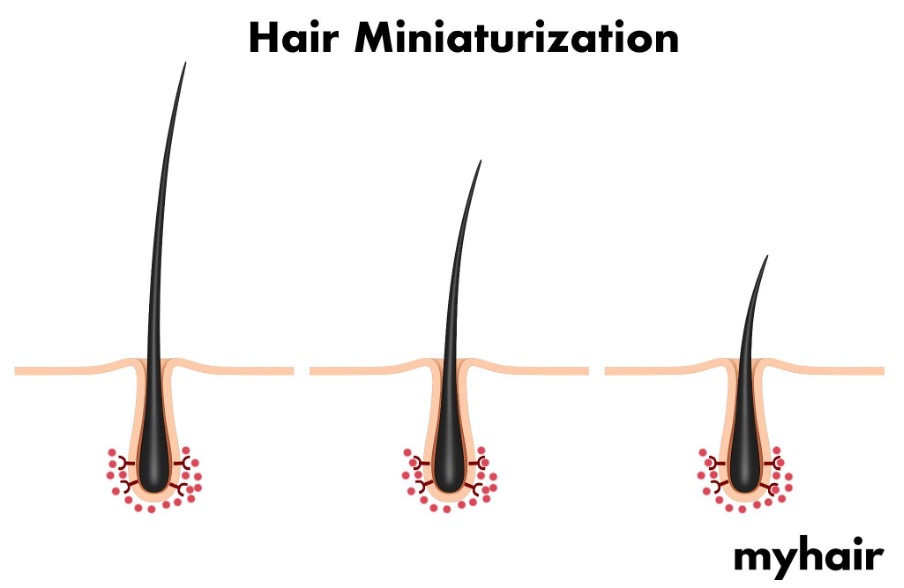
DHT isn’t generally harmful. And although people often say that excess DHT is the culprit behind hair loss, it isn’t a build-up of this hormone that causes androgenic alopecia. Hair loss occurs to some people when DHT binds to their hair follicles.
When DHT binds to a person’s follicles, they start experiencing the first signs of hair loss. These symptoms start out gradually, initially causing thinner, shorter, and weaker hairs. As androgenic alopecia is progressive, these hair loss symptoms gradually get worse. If a treatment isn’t started, hair follicles will eventually stop producing hair altogether.
It’s quite ironic that DHT can produce too much hair on your body while simultaneously causing hair loss on your head. Fortunately, DHT blockers for hair loss can be used to resolve these issues.
What are DHT blockers?
DHT blockers essentially stop the body from converting testosterone into DHT. Most DHT blockers typically target one or two receptors from the 5-αR enzyme family, rather than testosterone or DHT directly.
A study in the journal Dermatologic Therapy reported that there are various types of DHT blockers. Some of them target a single receptor type within the 5-αR enzyme family, while others target multiple receptor types.
This is important as it means that not all DHT blockers are created equally. Some are stronger than others. Generally, medications like finasteride and dutasteride are considered to be much more potent than herbal DHT blockers or the nutraceuticals used to make DHT blocker supplements.
Do DHT blockers actually work?
DHT blockers really do work! They’re approved for the treatment of several health issues, including prostate problems and androgenic alopecia. In fact, finasteride, which is one of two FDA-approved medications for male pattern hair loss, works by targeting a single receptor of the 5-αR enzyme.
Another well-known hair loss DHT blocker is dutasteride. Unlike finasteride, which mainly targets a single receptor, dutasteride works by mainly targeting two types of 5-αR enzyme receptors. This medication is approved for the treatment of androgenic alopecia in Japan and South Korea.
Dutasteride is FDA-approved for the treatment of enlarged prostates, but is not yet approved for the treatment of hair loss in the USA. However, the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology reported that it is still considered to be a valid hair loss treatment among dermatologists as it’s much stronger than finasteride.
Natural DHT blockers
DHT blockers aren’t only found in medications. They also occur naturally. You can find natural DHT blockers in food, beverages, and supplements. There’s a good chance you eat or drink some of them on a regular basis.
The study in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology and studies in the Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery, Andrologia, and Nutrients reported that many herbs and plants are natural DHT blockers. These include:
- Saw palmetto (Serenoa repens/serrulata)
- Equisetum species (particularly horsetail – Equisetum debile)
- Stinging nettle (Urtica dioica)
- Lingzhi mushroom (Ganoderma lucidum)
- East Indian globe thistle (Sphaeranthus indicus Linn.)
- Giant dodder (Cuscuta reflexa Roxb.)
- Wax gourd/Winter melon (Benincasa hispida Cogn.)
- Black pepper (Piper nigrum)
- Lesser galangal (Alpinia officinarum)
- Japanese climbing fern (Lygodium japonicum)
- Oyster mushrooms (Pleurotus ostreatus)
- Shiitake mushrooms (Lentinula edodes)
Keep in mind that these are all herbs and plants with DHT blocking properties. Most of them haven’t been clinically tested the same way that finasteride and dutasteride have. Their strength is thought to be weak or may still be unestablished. Out of all of these, the most thoroughly tested natural DHT blocker is saw palmetto.
Saw palmetto as a DHT blocker
Saw palmetto extract – specifically taken from this plant’s berries – is a commonly used nutraceutical and popular natural DHT blocker. This plant is thought to work in a similar manner to finasteride, preventing testosterone from converting to DHT by blocking part of the 5-αR enzyme pathway. You can find saw palmetto used in a wide variety of hair loss products, including DHT blocking shampoo, anti DHT cream, and nutrient supplements.
A handful of studies have found that saw palmetto products can help improve hair growth, hair density, and scalp health in people with pattern baldness. But research is still new and limited. More studies are needed to truly understand how well natural DHT blockers work and which products work best.
In the meantime, though, there’s nothing wrong with trying one of these natural products. And of course, feel free to keep on incorporating edible DHT blockers into your diet. Drinking nettle tea, cooking mushroom stir frys, and grinding black pepper over your food are all perfectly safe ways of incorporating natural DHT blockers into your day to day life. Just don’t rely on natural DHT blockers as your only hair loss treatment.

Natural DHT blockers, like shiitake mushrooms, may already be a normal part of your diet
When Don’t DHT blockers work?
DHT blockers usually work for people with male pattern hair loss – but they don’t always work for everyone. And to make matters more complicated, you might respond to one type of DHT blocker and not another.
For example, an article in the International Journal of Dermatology found that the majority of their study’s participants (77 percent) saw hair regrowth after taking dutasteride to treat androgenic alopecia. These same participants had previously taken finasteride for 6 months without seeing any positive effects.
It’s also important to remember that hair loss can be due to more than androgenic alopecia. According to a study in the Journal of Clinical Trials & Research, not everyone with hair loss has elevated levels of DHT. This is particularly true for hair loss that occurs due to alopecia areata (an autoimmune condition) or stress-induced hair loss.
For example, some people with pattern baldness end up having hair loss that’s caused by other factor, like, inflammation, immune system issues, or poor nutrition. All of these things can affect the hair growth cycle. These factors can make people’s hair follicles particularly sensitive to DHT. This androgen consequently ends up affecting their hair follicles even though they have normal hormone levels.
In these cases, DHT-blockers may not work so well. Instead, choosing healthier foods, managing lifestyle issues like stress or lack of sleep, and reducing exposure to allergens may be able to help. If you’re not certain of the cause behind your hair loss, talk with your doctor. They can determine if your DHT levels are elevated and help you figure out the right treatment plan.
DHT Blocker Effectiveness vs. Side Effects
DHT blocking medications definitely work, but potent drugs like finasteride and dutasteride tend to cause well-known side effects. In contrast, less is known about the effectiveness of natural DHT blockers. However, few to no side effects are ever reported from nutraceutical products.
Finasteride and dutasteride
Both oral finasteride and dutasteride are well tolerated, according to the study in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology. However, they’re also known to cause sexual side effects.
One study found that side effects like decreased libido, smaller amounts of ejaculate, and erectile dysfunction occurred in as many as 15.8 percent of participants. Finasteride and dutasteride might certainly give you back your luscious head of hair, but are they really worth taking if they throw your libido out the window?
Many people who take medications like finasteride and dutasteride find that sexual side effects decrease as their bodies get used to the medication. However, this isn’t always the case. Some people continue to experience multiple unpleasant side effects even after they stop taking DHT blocking medications.This particularly rare cluster of side effects is referred to as post-finasteride syndrome.
Despite the name, post-finasteride syndrome can occur to both finasteride and dutasteride users. At the moment, this issue isn’t acknowledged by all scientists and medical professionals. However, it’s being increasingly reported in medical literature, and the National Institutes of Health have included information about this condition in its Genetic and Rare Disease Information Center.
The main way to avoid finasteride and dutasteride’s serious side effects is to simply not take these medications orally. According to a review in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology, topical DHT blockers, including finasteride and dutasteride, don’t cause the same serious side effects as oral DHT blocking medications. This review even mentioned a study that successfully combined topical finasteride and dutasteride without causing any issues.
If topical finasteride and dutasteride are so effective and harmless, you’re probably wondering what their downside is. Well, these alternative versions of these medications are still in the research phase. There are currently no topical formulations that are FDA approved or even regularly available for off-label use. This makes them hard to obtain, unless you can get them specially prepared by your pharmacist.
Plant-based DHT blockers
Natural DHT blockers typically work without causing side effects. Unfortunately, research on the effectiveness of most of these plants and nutraceuticals is limited. There are also very few studies that compare the effectiveness of DHT blocking medications with natural DHT blockers. However, the studies that do exist – particularly those related to saw palmetto – seem promising.
For example, one study, published in the International Journal of Immunopathology and Pharmacology, assessed people taking saw palmetto supplements over a two-year period. These researchers found that 38 percent of people using saw palmetto had improved hair growth. However, a study in the Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, which used a lower dose of saw palmetto but combined it with a nutritional supplement, reported that 60 percent of people in their study had improved hair growth.
Newer studies are now studying the effectiveness of saw palmetto in different formats. For example, a study in the Australasian Journal of Dermatology tried using a combination of saw palmetto serums, lotions, and shampoos over a 24-week period and found very promising results. That being said, it acknowledged that people responded to some products better than others.
There’s still a lot of research to be done before a standardized saw palmetto treatment option can be recommended. However, saw palmetto is generally recognized as a potential treatment option for male pattern hair loss. Its lack of side effects — particularly sexual ones — will continue to make it popular in people who want to avoid finasteride.
What’s the best DHT blocker for you?
Out of all the DHT blockers available, finasteride is the only one that’s currently approved by the Food and Drug Administration. But if you’re wary of it’s side effects, you may prefer a nutraceutical DHT blocker, like saw palmetto.
Although they may operate in different ways, medications like finasteride and dutasteride are thought to work in a similar manner to plant-based DHT blockers, like saw palmetto. However, be aware that natural DHT blockers are much weaker than DHT blocking drugs.
Despite being weaker, natural DHT blockers are still an appealing choice because they have no known major side effects. In contrast, DHT blocking medications can have serious, long-term side effects — unless they’re used as creams or lotions. Unfortunately, topical DHT blocking drugs are not yet easily available for most people to obtain.
Regardless of the DHT blocker or other hair loss treatment you choose, there’s nothing wrong with integrating natural DHT blockers into your diet. In fact, you may already be putting foods like galangal in your Thai curries, mushrooms in soups or stir fries, and winter melon in your stews.